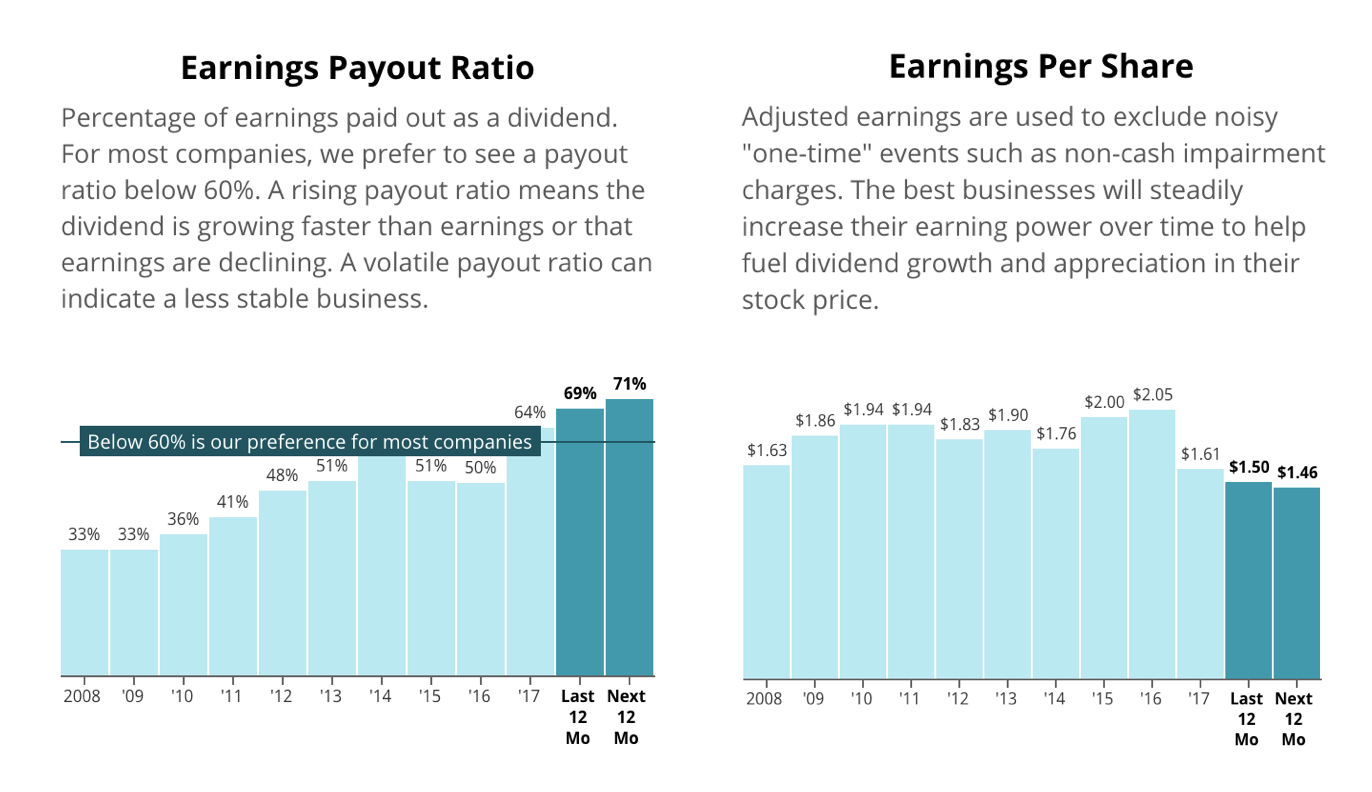
In order to understand the purpose of this article, it helps to know about dividend distributions. Dividend distribution is a payment made to the shareholders in a publicly traded company or mutual fund. To the shareholder, this is a dividend income. How these are taxed is determined by the length of time they are held by the investor. (Harvey, C., 2012).

Companies that make money like to give their investors an incentive to join the company. One incentive that is given is in the form of dividend distributions. There are various ways to distribute dividends from a company. The IRS explains the various types of distributions used. The most common way of paying these dividends is cash. Stock in another company is also a way that dividends are distributed or as any other property. Other forms of payout through an interest in a partnership, an estate, a trust, a subchapter S corporation, or from an association that is taxable as a corporation. (IRS, 2016).
The cash dividend is a payment in a certain amount of cash to those investors holding the company’s stock on a specific date. A stock dividend is when common stock is issued to the shareholders without consideration. Property dividend is a non-monetary dividend paid to investors, rather than cash or stock payment. Scrip dividend is a promissory note to pay shareholders at a later date. This creates a note payable. Liquidating dividend is when the board of directors returns the capital originally contributed by shareholders as a dividend.

Dividend distributions have become a very commonly used tool in today’s economy. There are a lot of benefits to using this incentive for both the company and the investors. It gives the investors something to look forward to each time it comes around. The company becomes more attractive to potential investors. The rates are not typically paid at the same rates.
There are two different types of corporations which use these distributions. One is a closely held corporation. A closely held corporation is any company that has only a limited number of shareholders. Closely held corporation stock is publicly traded on occasion, but not on a regular basis. These entities differ from privately owned firms that issue stock that is not publicly traded. (Investopedia, 2016).

Public companies are best defined in the next few sentences. The term “public company” can be defined in various ways. There are two commonly understood ways in which a company is considered public: first, the company’s securities trade on public markets; and second, the company discloses certain business and financial information regularly to the public. (Investor, 2016). The rates of distributions vary depending on the company.
One consideration is the use of a dividend policy, which is viewed as irrelevant to some people. This is because investors have the ability to create “homemade dividends”. The second consideration is a no dividend payout. They decide this because the taxation on a payout is higher than the tax for a capital gain. Other investors look at a high dividend payout as a way to provide certainty about the company’s financial wellbeing.

There are two methods that a company considers using, high or low dividend method. There are three different approaches: residual, stability or a hybrid compromise. The residual policy relies on internally generated equity. The stability allows the company to choose a cyclical policy that sets dividends are set at a fraction of yearly earnings. The hybrid approach combines both the residual and stability policies together. The company looks at the debt/equity ratio as a long-term instead of a short-term goal. (Investopedia, 2016).
The companies each use their own type of dividend distribution, and some don’t use them at all. The high tax rate on dividend payouts compared to capital gains are a negative factor towards choosing to go with the policy. With the economy the way it is, companies have various options for dividend policies. The choices made by the company depend on how they want to attract investors. It also gives them a variety of choices on how to keep investors interested in staying. Having this information will help get a good idea on how to deal with the companies and investors.
References
Accounting Tools (2016) Types of Dividends. (NPG) Retrieved from: http://www.accountingtools.com/types-of-dividends
Harvey, Campbell (2012) Dividend Distribution. (NPG.) Retrieved from: http://financial-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Dividend+distribution
Investopedia (2016) Closely Held Corporation (NPG). Retrieved from: http://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/closely-held-corporation.asp
Investor.gov (2016) Public Companies (NPG). Retrieved from: https://www.investor.gov/introduction-markets/how-markets-work/public-companies
IRS (2016). Topic 404-Dividends (NPG.) Retrieved from: https://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc404.html